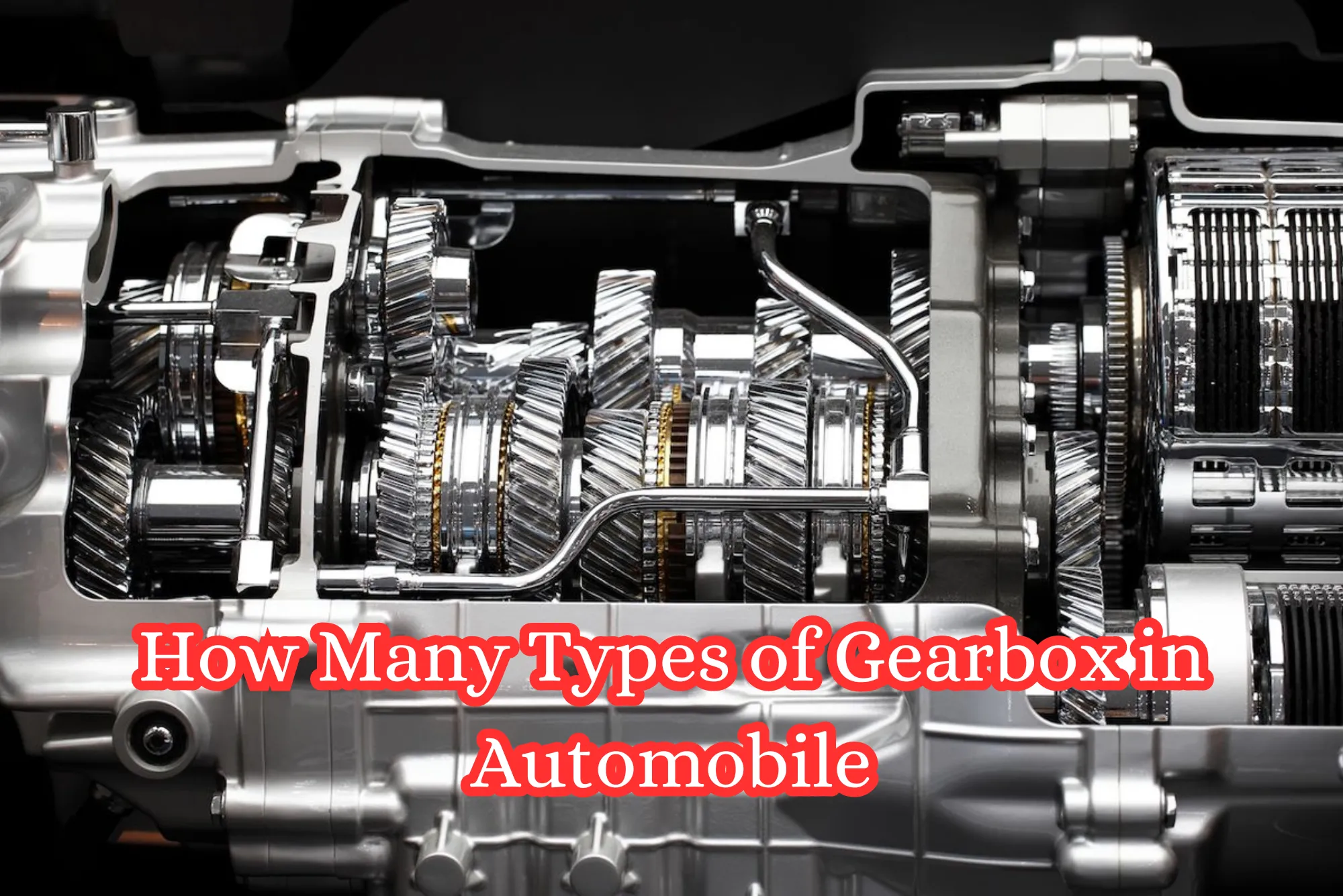
Introduction to How Many Types of Gearbox in Automobile
In the realm of automobiles, the gearbox plays a pivotal role in transmitting power from the engine to the wheels. Understanding the different types of gearboxes is essential for both enthusiasts and drivers. Let’s delve into the fascinating world of automotive gearboxes and explore their types, functions, and applications.
Manual Gearbox
A cornerstone of traditional automotive engineering, the manual gearbox, or manual transmission, requires the driver to manually shift gears using a gear stick and clutch pedal. Each gear provides different speed and torque ratios, offering the driver greater control over the vehicle’s performance. Despite the proliferation of automatic transmissions, manual gearboxes remain popular among purists and performance-oriented drivers for their engaging driving experience.

Automatic Gearbox
In contrast to manual transmissions, automatic gearboxes employ a fluid coupling or torque converter to automatically shift gears without manual intervention. These transmissions offer convenience, especially in stop-and-go traffic, as they eliminate the need for manual gear shifting. Modern automatic transmissions feature advanced electronic controls, offering smooth gear changes and improved fuel efficiency.
Continuously Variable Transmission (CVT)
Continuously Variable Transmissions (CVTs) represent a departure from traditional gearboxes. Instead of fixed gear ratios, CVTs use a system of pulleys and belts to provide seamless acceleration by infinitely varying the transmission ratio. This results in smoother driving dynamics and enhanced fuel efficiency. CVTs are increasingly common in modern vehicles, particularly hybrids and compact cars.
Dual-Clutch Transmission (DCT)
Dual-Clutch Transmissions (DCTs) combine the efficiency of manual gearboxes with the convenience of automatic transmissions. Unlike traditional automatics, DCTs utilize two separate clutches—one for odd-numbered gears and the other for even-numbered gears—to pre-select the next gear. This allows for lightning-fast gear changes, providing a sporty driving experience while optimizing fuel economy.
Automated Manual Transmission (AMT)
Automated Manual Transmissions (AMTs) bridge the gap between manual and automatic gearboxes. Similar to manual transmissions, AMTs feature a conventional gearbox with a clutch system. However, the clutch and gear shifts are actuated electronically or hydraulically, eliminating the need for manual clutch operation. AMTs offer the efficiency of manual transmissions with the convenience of automatics, making them popular in entry-level vehicles.

The gearbox is an integral component of every How Many Types of Gearbox in Automobile, dictating its performance, efficiency, and driving experience. Whether you prefer the tactile engagement of a manual gearbox or the seamless shifts of an automatic transmission, understanding the different types of gearboxes empowers you to make informed decisions when choosing your next vehicle. Embrace the diversity of automotive engineering and enjoy the ride, whatever gearbox you may choose.
Automobile Chassis
The automobile chassis serves as the structural backbone of a vehicle, providing support for the vehicle’s components and passengers. It comprises the frame, suspension system, steering mechanism, and wheels, among other elements. A well-designed chassis ensures stability, handling, and safety, forming the foundation for a superior driving experience.
best auto parts m7 main br.
Finding the best auto parts, especially for critical components like the best auto parts m7 main br. bearing, is essential for maintaining your vehicle’s performance and longevity. Ensure that you source parts from reputable manufacturers or suppliers to guarantee quality, compatibility, and reliability. Invest in genuine OEM parts or high-quality aftermarket alternatives to optimize your vehicle’s performance and minimize the risk of premature failure.